Technology has revolutionized not just IT but also healthcare, making the diagnosis of severe conditions like gastrointestinal perforation more accurate and manageable. At SH Binayak Multi-speciality Hospital, we utilize cutting-edge equipment to ensure you receive specialized care. Our leading GI surgeons in Kolkata provides insights into the latest diagnostic tools our team uses.
What is gastrointestinal perforation?
A gastrointestinal perforation is a medical condition in which a hole forms inside the gastrointestinal tract. The GI tract helps in passing food and digestion. It includes a series of organs, such as the stomach, esophagus, small intestine, and large intestine.
- Stomach- digestion of food
- Esophagus- transports food to the stomach
- Small intestine- digestion and absorption of nutrients
- Large intestine- converts undigested food into stool
How does gastrointestinal perforation affect?
A perforation or hole in the gastrointestinal tract requires immediate care as it can be severe. It can lead to stool leaking into the abdomen or food or digestive nutrients leaking into the abdomen if the hole is present in the small intestine. Some of the major side effects of GI perforation includes-
- Internal bleeding
- Swelling of the inner abdominal wall
- Infection
- Damage to the gastrointestinal tract
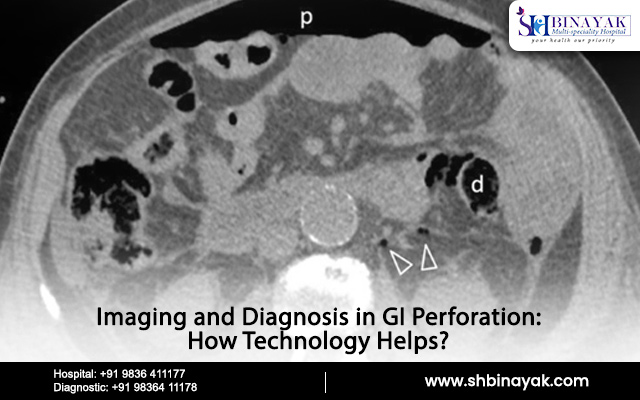
Imaging and Diagnosis
If you are diagnosed with gastrointestinal perforation, an immediate surgery is required. It helps in pinpointing the location and extent of perforation. Here’s how a GI surgeon in Kolkata addresses your issue.
1. X-rays
X-rays can reveal free air in the abdominal cavity, a common sign of GI perforation. They provide a quick and initial assessment.
2. Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
CT scans offer detailed cross-sectional images of the abdomen, allowing doctors to see the exact location and size of the perforation. They can also show the extent of leakage and associated complications like fluid accumulation or inflammation.
3. Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the abdominal organs. It helps detect free fluid and gas, which can indicate perforation. It’s often used in emergency settings due to its speed and lack of radiation.
4. Endoscopy
In some cases, a flexible endoscope is used to inspect the inside of the GI tract visually. This can help identify the perforation directly, though it’s less common for initial diagnosis.
5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is less frequently used but can provide detailed images of soft tissues. It’s helpful in complex cases where other imaging methods might not be sufficient.
Conclusion
These imaging technologies are vital in accurately diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal perforation. Experienced GI surgeons in Kolkata at SHBinayak Multi-speciality Hospital provide tailored treatment plans that best suit their patients’ needs for effective treatment and recovery.